Tactic 22. Construct Peering from Transit
Peering can be constructed from transit by filtering out all noncustomer routes as shown in Figure 11-37.
Engineers can look at routing tables and see where there are adjacencies. A peering relationship may be inferred in a situation where only customer routes appear.
Why would you do this? So you appear more attractive. Target peers may believe that you are peering with the big players when they look at the routing table. If the big players find you worthy of peering, then perhaps the target ISP will believe that it should as well.
Just like Paid Peering, constructing peering from transit is like paying for a date to the prom.
In this tactic, only the two parties know there is a cash payment at the end of the evening. Nondisclosure agreements are generally applied to Paid Peering, and neither party is motivated to disclose its nature. The purchaser wants to appear to be a true peer, and the provider doesn’t disclose its nature because it wants to continue getting the revenue for it.
The real challenge is that the target peer that you want doesn’t have a Paid Peering product, but it would love to sell you transit. So you can construct peering out of transit by filtering all noncustomer routes.
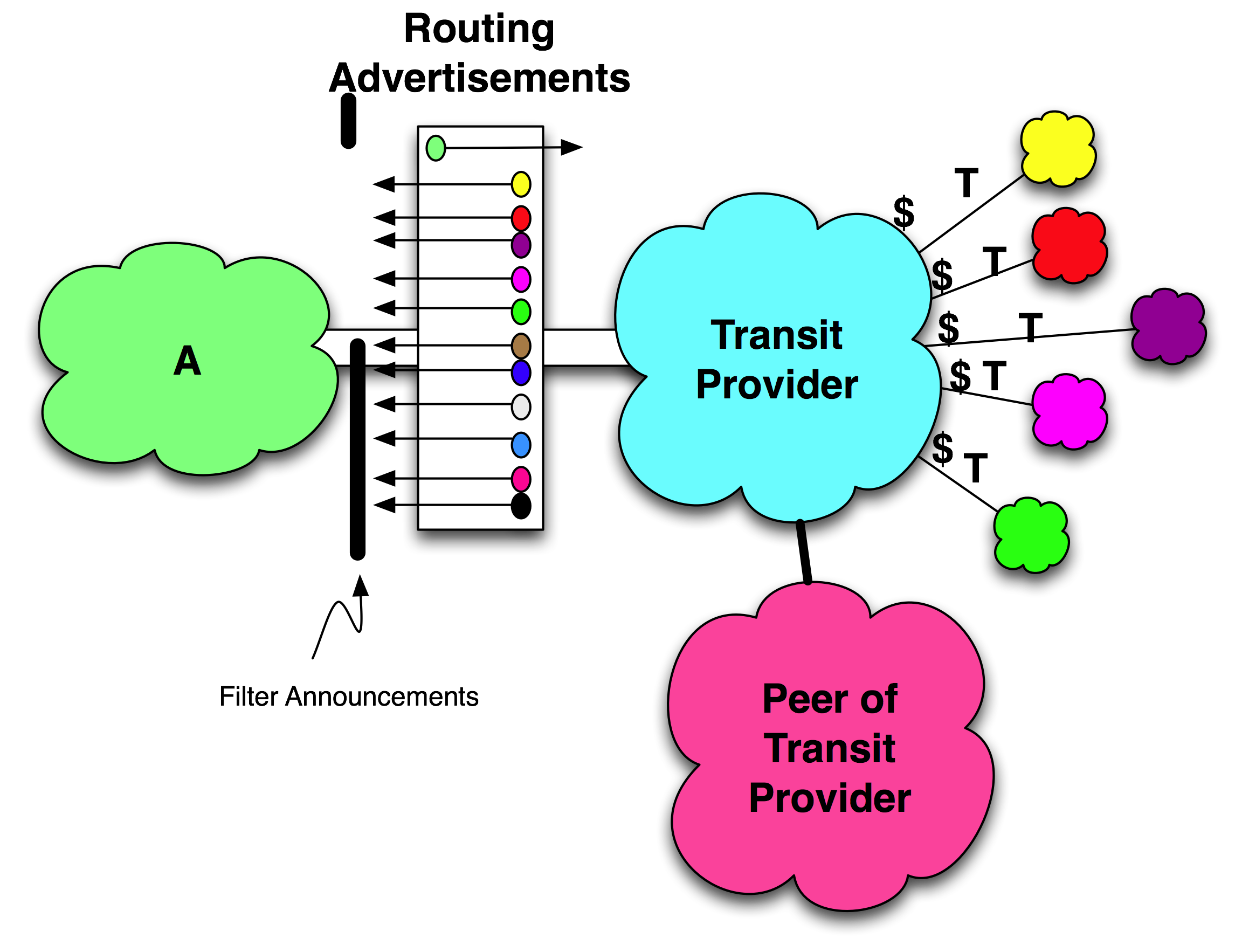
Figure 11-37. Filtering noncustomer routes appears to be peering in the routing table.

